Key Takeaways:
-Blum video task November 18-19: “Smart Contracts 101 Blum”, Code: SMARTBLUM
-A smart contract is a decentralized blockchain program that automatically executes agreements based on set conditions.
-The most comprehensive summary of Blum video codes are available on WEEX Help.

Contents
Smart Contracts 101 Blum Code November 18
The Blum Academy has released “What Are Smart Contracts? How They Work in Blockchain,” video on November 18. This Smart Contracts 101 Blum video dives into the future of transactions, breaking down the revolutionary technology behind smart contracts. Discover how these “automatic agreements” are transforming crypto, business, and beyond—reshaping industries and eliminating the need for middlemen!
Smart Contracts 101 Blum Video Code Task:
Video: Smart Contracts 101
Blum Code : SMARTBLUM

What Are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing digital agreements with terms directly written into their code. First introduced by computer scientist Nick Szabo in the 1990s, their functionality gained prominence with blockchain platforms like Ethereum.
These contracts operate on decentralized blockchain networks, eliminating the need for centralized control. They execute predefined conditions automatically, ensuring accurate, timely, and tamper-proof results. By removing intermediaries, smart contracts reduce counterparty risk, enhance efficiency, and increase transparency in multi-party agreements.
Key Features of Smart Contracts 101:
- Decentralized: Operate on blockchain networks, reducing the risk of tampering or centralized control.
- Immutable: Once deployed, the code cannot be altered, ensuring integrity and transparency.
- Self-Executing: Automatically trigger actions when predefined conditions are fulfilled.
For example, a smart contract can release escrow funds only when both a buyer and seller confirm successful delivery, showcasing its utility in automating processes and fostering trust.
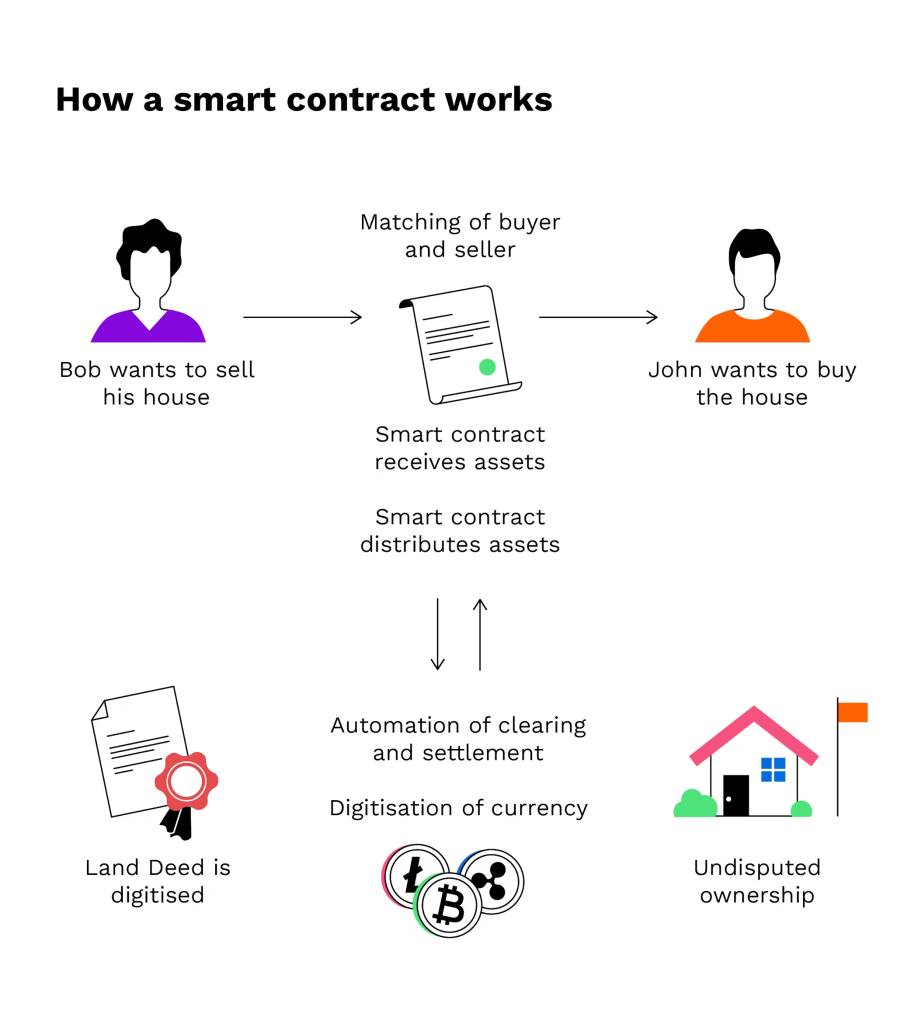
Types of Smart Contracts: An Overview
Smart contracts fall into three main categories: smart legal contracts, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and application logic contracts (ALCs). Each type leverages blockchain technology to drive transparency, efficiency, and automation. Here’s a closer look:
1. Smart Legal Contracts
Smart legal contracts resemble traditional agreements, following an “if this, then that” structure. These blockchain-based contracts are legally binding and offer greater transparency compared to conventional methods.
Executed using digital signatures, smart legal contracts automatically trigger actions, such as releasing payments, when predefined conditions are met. Non-compliance, however, may lead to legal repercussions. This automation and enforceability make them highly efficient and trustworthy.
2. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are blockchain-governed organizations without centralized leadership. Instead, smart contracts define rules and voting rights, ensuring transparency and collective decision-making.
DAOs aim to achieve shared goals through community-driven governance. A prime example is VitaDAO, which uses smart contracts to support decentralized scientific research funding. DAOs demonstrate how blockchain can transform organizational structures and resource management.
3. Application Logic Contracts (ALCs)
ALCs are designed for application integration, enabling seamless interaction between blockchain contracts and systems like the Internet of Things (IoT). Unlike legal contracts or DAOs, ALCs facilitate machine-to-machine communication, automating tasks and data sharing without human involvement.
These contracts unlock innovative use cases, streamlining processes in technology and industrial applications.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
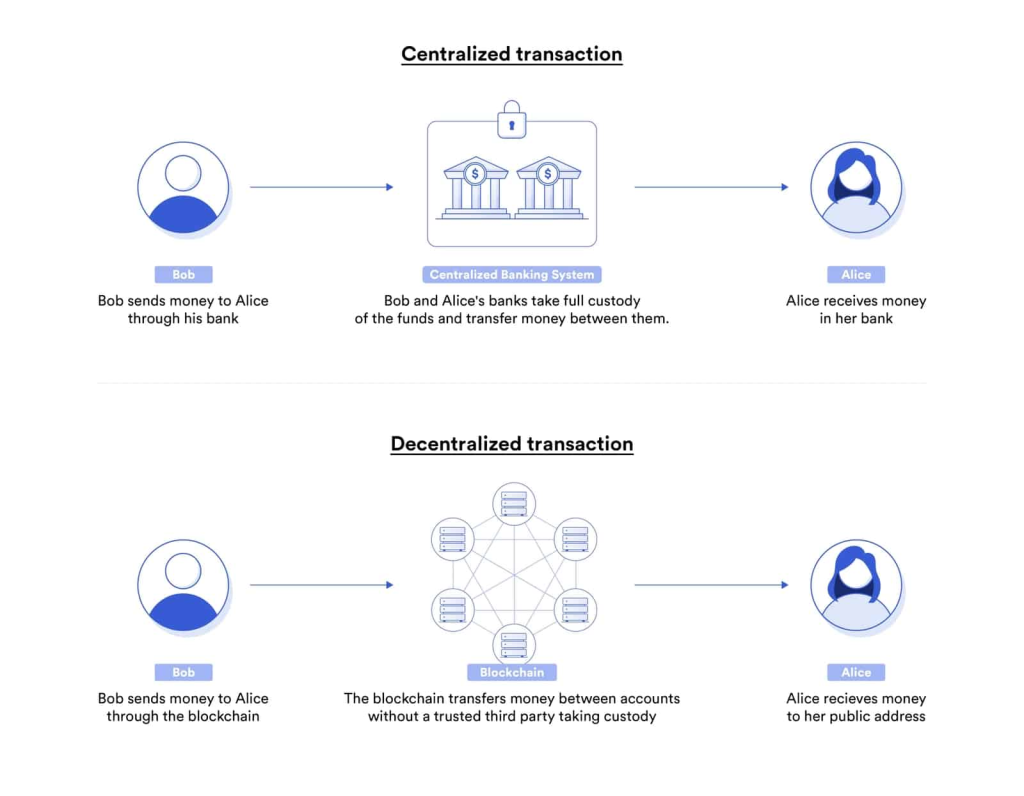
Traditional digital agreements typically require centralized intermediaries, such as banks, to enforce terms and reduce counterparty risk. While this model facilitates agreements between unfamiliar parties, it often creates inefficiencies and grants intermediaries disproportionate influence. Smart contracts overcome these limitations by leveraging blockchain technology, offering several key benefits:
1. Robust Security
Smart contracts operate on decentralized blockchain networks, removing single points of failure and minimizing risks of tampering or manipulation. This ensures that neither party nor any central authority can alter the contract’s terms or interfere with its execution.
2. High Reliability
Decentralized networks process smart contracts across multiple nodes, ensuring accurate and consistent execution. This redundancy guarantees that agreements are carried out as specified, providing a trustworthy and tamper-proof solution.
3. Enhanced Fairness
With no reliance on profit-driven intermediaries, smart contracts level the playing field for participants. Decentralized enforcement prevents middlemen from extracting excessive fees or exploiting their position of power.
4. Streamlined Efficiency
Smart contracts automate processes such as escrow, execution, and settlement, removing the need for manual input or intermediary approval. This automation speeds up transactions and reduces delays, ensuring smoother operations.
By replacing centralized intermediaries with decentralized automation, smart contracts offer a transformative approach to digital agreements, delivering unparalleled security, fairness, and efficiency.
Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are versatile, finding applications in various industries:
- Finance and Banking: Automating processes like loan disbursement, insurance claims, and cross-border payments.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods in real time, ensuring transparency and authenticity.
- Real Estate: Facilitating property transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries like agents or escrow services.
- Healthcare: Securing patient data and streamlining billing and insurance processes.
- Gaming and NFTs: Powering decentralized applications (dApps) and enabling secure ownership transfers of digital assets.
As blockchain adoption grows, the scope of smart contract applications will continue to expand, revolutionizing traditional systems.
Understanding Smart Contracts 101 on WEEX
WEEX is gaining recognition as an excellent crypto exchange for beginners due to its user-friendly platform, security measures, and extensive educational resources. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned trader, WEEX offers a seamless trading experience with support for various cryptocurrencies, including BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT, DOGE/USDT, XRP/USDT, WXT/USDT SOL/USDT and other numerous altcoins. Beyond trading, WEEX is dedicated to educating its users, making it a trusted resource for those looking to stay informed in the fast-paced world of crypto.
Staying Informed: Smart Contracts 101 Blum Updates on WEEX
What is Slippage Blum Code: What is Slippage in Crypto
Understanding Gas Fees Blum Code: What Are Gas Fees?
Node Sales in Crypto Blum Codes: A Beginner’s Guide to Node Sales
Crypto Slang Part 2 Blum Code: Key Crypto Slang You Need to Know
Find us on:
Sign up for a WEEX account now: https://www.weex.com/register
[Supported Platforms]:
